CNC MachiningNC MachiningCNC Machinin
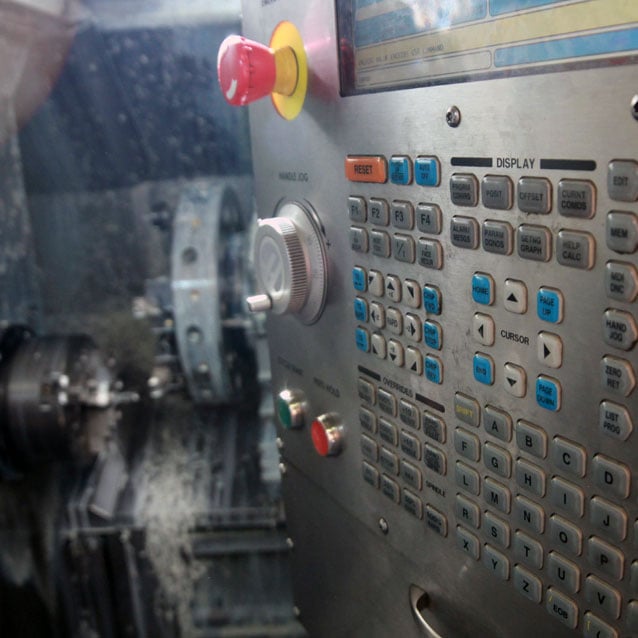
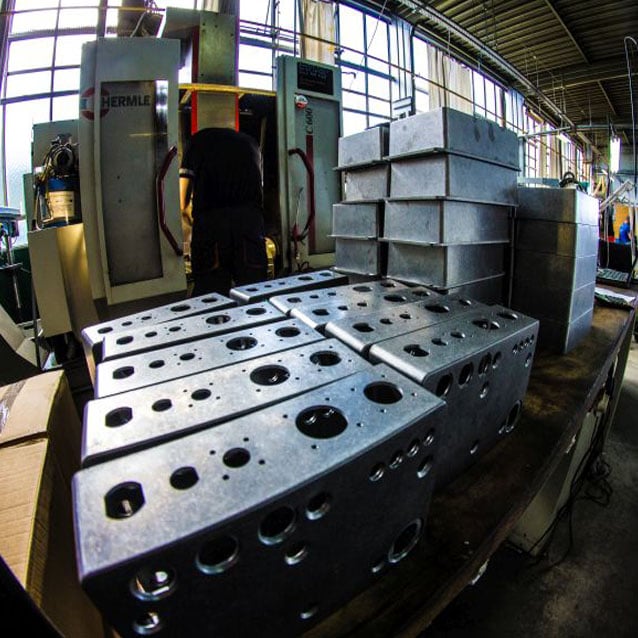
Machining on CNC machines is a specialty and main area of our company's activity. We offer 3-axis and 5-axis machining. The multifunctional 5-axis Takisawa turning center is equipped with two opposing spindles and two tool head / milling head. It will provide a very wide range of processing options and ensures very high quality and accuracy of processing. The 5-axis Hermle milling center enables the production of details that require one clamping to achieve the expected accuracy. The large format of the working surface of the milling plotter allows easy and quick use of whole sheets of materials without the need to format them, and the vacuum table ensures easy processing of even very thin boards. Our employees have the necessary knowledge, skills and experience, which, supported by the capabilities of the machine park, ensure wide production possibilities for the most demanding customers.
Machining technological processes.
Milling
Milling is one of the basic machining processes. Nowadays, for milling, technologically advanced numerically controlled machines, commonly known as CNC milling machines, are used.
The milling process enables the production of: planes, grooves, slots, shaped surfaces, threads and teeth.
Thanks to the use of multiple blades in the tool, milling is very efficient. Each of the blades performs work at certain times, which allows the heat to drain into the tool body while the blade passes through the idle path. The problem, however, is the occurrence of stresses in the blade material, which may result in vibrations in the machine tool - tool - workpiece system.
The basic types of milling types, broken down by the arrangement of cutting blades, are distinguished by:
- Face milling
The blades are arranged on the frontal and peripheral surfaces. - Peripheral millin
The blades are located only on the peripheral surface. As a curiosity, it should be added that nowadays face milling almost completely replaces peripheral milling, which is dictated by many advantages of face milling, such as: greater surface smoothness and dimensional accuracy, more stable operation of the milling machine and greater process efficiency.
- Oblique milling
The milling cutter axis makes an angle in the range of 0 to 90 degrees in terms of the machined surface.
The basic treatments of the milling process are:
- Face milling.
- Shoulder and face milling.
- Profile milling.
- Profile milling of pockets.
- Milling grooves.
- Frezo-turning.
- Thread milling.
- Milling narrow slots and parting.
- High feed milling.
- Plunge milling.
- Ramping.
- Helical ramping.
- Movement along an arc of a circle.
- Trochoidal milling.
Turning
CNC turning is another of the basic machining processes. Turning is mainly used for processing metals, plastics and wood. In the past, this process was performed manually on a lathe, and now the production of turned parts is almost completely automated and is done on CNC lathes. CNC * abbreviation Computerized Numerical Control means "computerized numerical control". Thanks to the current computer control technology, CNC machines are able to automatically produce very complex parts with extremely high repeatability.
In classical turning, mainly round parts are machined and produced. Interestingly, the latest technology of CNC lathes also allows the balancing of turned parts that were previously only produced on milling machines. Currently, lathes are often used to manufacture microscopic parts used, for example, in the medical, microtechnology or watchmaking industries.
The basic methods of this machining are CNC turning divided into the point method, the shape method and the envelope method.
The basic turning procedures include:
- Longitudinal turning.
- Face turning.
- Shaped lanes.
- Turning cones.
- Threading, drilling and knurling.